
Markings / Colors / Camouflage

| The
early prototypes of the A4/V2 were painted in the familiar black-and-white
roll pattern scheme. This scheme was designed to aid in tracking the rocket
after launch. This pattern made it easy to observe any variation or roll
of the rocket. The exact pattern was changed many times, and as with the
rest of the rocket, the pattern was examined and altered if warranted-
Camouflage colors were introduced to the A4/V2 during the middle of 1943. At the beginning, three different schemes were designated to be tested- SCHEME 1 - The Gebatikt (Batiked) pattern, using 5 colors: Cream White, Earth Grey, Oxide Red, Olive Green and Chocolate Brown. This scheme was sprayed and was simular to many traditional camouflage patterns. SCHEME 2 - The Geflammt (Wavy) pattern, using only three colors: Cream White, Earth Grey and Olive Green. SCHEME 3 - The Gezackt (Ragged) pattern, using the same three colors as scheme 2. Actually, there were two versions of this ragged scheme. The second version bacame the most popular, and was adopted in March of 1944. Cream White was replaced with Signal White and the ragged pattern simplified. Of the surviving photographs showing A4/V2 rockets using the ragged camouflage scheme, the majority of these are the later ragged scheme- Later, during the waining months of the war, all A4/V2 rockets were painted a solid color of Olive Green only. Some Dutch eyewitnesses reported solid Cream White only rockets. The colors were the same colors used by the German Army throughout WWII. The eight RAL Reichsausschuss für Lieferbedingungen (Government Committee for Specifications) colors were identified by number as; RAL 9001 Cream White, RAL 9003 Signal White (Humbol 28+34) (Revell 5+371), RAL 7028 Earth Gray (Humbrol 94) (Testors 2095) (Tamiya XF55), RAL 3039 Oxide Red, RAL 6003 Olive Green (Testors E7733) (Humbrol 117) (Revell 361) (Tamiya XF58) (This has also been shown to be RLM 71 Olive Green - Testors 2081), RAL 8017 Chocolate Brown, RAL 9010 Clear White, and RAL 9011 Graphite Black. Note:
RAL 9001 Cream White and RAL 9003 Signal White are not really 'white' at
all.
Army
rockets did not carry the national aircraft or unit insignia. But, many
of the Peenemünde test rockets did carry cartoon illustrations. These
illustrations were simular to WWII aircraft nose art in design and connotation.
Undoubtedly, many operational A4/V2 rockets probably carried hand-scribbled
messages directed in jest, toward their intended recipients. Many operational
V2s did have their army serial numbers painted on the body of the rocket
near the upper section, as well as the lower section, adjacent to the fins.
|
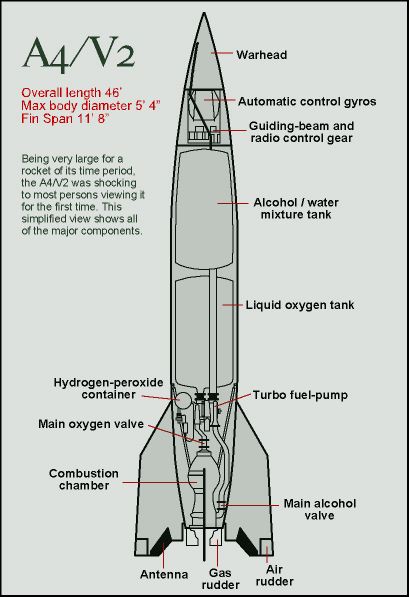
Click here to view a large diagram of the A4/V2 engine systems Before launch, the empty V2 weighs 10,000 lbs (4539 kg), it is filled with fuel, alcohol, liquid oxygen, hydrogen peroxide en sodium permanganate (catalyst). The air batteries and nitrogen batteries are filled up to 200 bar, and the rocket now weighs 28,000 lbs (12700 kg). Electrical cables are now connected and gyroscopes are being powered up by 28 Volts / 60 Amps, DC. The cables are connected till launch, batteries take care of power supply during flight. After everything is set, pressurized air (32 bar) presses the hydrogen peroxide and the sodium permanganate into the 580 HP turbine. This causes the turbine to rotate 3800 per min. This turbine moves two pumps that inject the Methyl alcohol, at 23 bar via 1224 nozzles (58 kg/sec) and liquid oxygen at 17.5 bar via 2160 nozzles (72 kg/sec) into the burn chamber at 23 bar. The mixture is ignited, where a temperature of 2500 degrees Celsius at 15 bar is reached, but is not producing enough impulse to lift the V2. Soon after checking to make sure propulsion is working properly, the burning speed will be raised and cables are disconnected electromagnetically. The
V2 engine burn chamber temperature was about 2700 degrees Celsius. This
wall is cooled by the liquid ethyl alcohol flowing via the double wall
of the beam tube and burning chamber, which also heated up the ethyl alcohol.
In the burning process, first oxygen is injected, without entering air,
then spontaneous burn of the fuel and liquid oxygen, then gasses flow with
great speed to the nozzle end. During burn time (about 60 sec) the V2 is
steered by 4 graphite rudders and 4 vanes (at the fins). To describe the
steering process, one can imagine the mechanics of the vertical vanes and
rudders 1 and 3, Fully fueled, the V2 had 4900 kg A-Stoff which was liquid oxygen with a temperature of minus 183 degrees Celsius, and 3710 kg of a mixture of 75% Ethyl alcohol and 25% water, called B-Stoff. The oxygen evaporated so quickly that the tank truck started at the load station with 6400 kg, so when they arrived at the site for V2 fueling, 1500 kg was already evaporated. The rocket also carried 175 kg of T-Stoff, which was 80% hydrogen, and 22 kg Z-Stoff which was a mixture of 1/3 part sodium permanganate and 2/3 part water. The latter was for propulsion of the 580 horsepower turbine, compressed air pushed those materials with a pressure of 32 bar in this turbine, 385 degrees Celsius vapor brought the turbine to 3800 RPM. Each second, 58 kg alcohol of 23 bars had to be pressed via 1224 injection ports, and 72 kg oxygen with a pressure of 17.5 bars via 2160 injection ports into the burning chamber, that eventually at a pressure of 15 bars brought the temperature to 2500 degrees Celsius. Initial lift pressure was 3 tons, which took 3 seconds (for observation of good ignition) and than raised to 25 tons. For the V2 , 6967 kg raw materials was needed (without the explosives and devices) of which 3112 kg thin sheet metal (various thickness) e.g. the outer skin. Average price of a V2 was 119600 Reichsmark. The A4/V2 rocket had an operational range of 234 miles. The max. burning time of the engine was 65-70 seconds, shortly before engine shutdown the A4 weighed 4040 kg at a height of 35 km, starting with 1 G force, and at shutdown 8 G, after shutdown the A4 flew to a height of 97 km and fell to earth with a impact speed of 3240-3600 km per hour. Liftoff was straight up; 30 seconds after launch it reached speed of sound. When launched against targets close to the operational range of the vehicle, the deviation between target and impact was normally 4 to 11 miles (7-17 km away from target). This made the rocket only suitable for use against widely populated areas. At shorter targeting ranges, the accuracy of the A4 was improved. The Leitstrahlstellung was a “guiding beam” that improved accuracy of the A4 somewhat during the later days of the campaign. One quarter of all A4 rockets were guided with the Leitstrahlstellung, only those launched by Batterie SS 500 from Dafsen/Hellendoorn area. A description of an A4/V2 impact would be as follows. First, a whip cracking sound of a blast wave created by the rocket (moving faster than the speed of sound) bounces off of the point of impact just split seconds before the flash of impact. This was followed by the chaos of the explosion with debris and earth churned skyward. Soon, the whine and rush of whistling air as the sound catches up with the rocket followed by a deafening roar of the incoming rocket, which tapers off to silence. There could be no warning. The A4/V2 impacted at 3 times the speed of sound. The V2 offensive would last from September of 1944 until March of 1945. Close to 2,500 rockets were launched in this time period. The London area was hit by over 500 rockets and several hundred more dropped in surrounding counties. At first London and Antwerp were the primary targets, but rockets also fell around Ipswich and Norwich, and many Allied held targets in France, Belgium and Holland, and even on Germany itself. Immediately
after the war, the V2 was extensively tested by the British during Operation
Backfire.
|
Statistics of the V2
| Power:
Liquid-fuelled rocket motor
Ethyl Alcohol (75%): 8179 lb, 3710 kg Liquid-oxygen: 10802 lb, 4900 kg Warhead: 1627 lb of explosives, 738 kg (not high explosives, because of frictional warmth exceeding 1200 degrees F during flight) Launch weight: 12.8 tons, 13000 kg Hydrogen Peroxide 285 lbs, 129 kg Sodium Permanganate 35 lbs, 15.8 kg Nitrogen 30 lbs (Nitrogen has multiple services, the difficult valve system is operated by it and the pressure in the alcohol tank is kept at a certain level). Thrust at liftoff: 55100 lb, 25,000 kg Fuel consumption, per sec: 286 lb, 130 kg Acceleration at liftoff: 0.9 g Burn time: 65 sec. Guidance: Gyro Preset |
Burning
temp. 4802 degrees F, 2650 degrees C
Consumption 276 lbs/per sec, 125 kg/per sec Max motor temp: ~2700 degrees C, ~4890 degrees F Motor pressure: 15 bar, 217 lb/sq inch Nozzle expansion ratio: 15.45:0.85 Warhead/Launch weight ratio: 0.075 Maximum speed: 5400 km/h, 3355 mph Maximum altitude: 96 km, 60 miles Length: 14 m, 46 feet Body diameter: 1.651 m, 5 ft. 5 inches Diameter over fins 3.55 m, 11 ft. 8 inches Rocket stays vertical after liftoff: 5 sec. -completes tilt within: 50 sec. -attains angle of 49 degrees from vertical at: 54 sec. -passes speed of sound: 25 sec. Velocity along trajectory (max): 1600 m / sec., 1 mi / sec. Impact velocity: 1100 m / sec., 3600 ft. / sec. Apogee of trajectory: 90 km, 56 mi Range: 320 km, 199 mi |
![]()